classroom instruction that works marzano

Overview of Classroom Instruction That Works
Marzano’s research-based strategies emphasize effective teaching methods to enhance student achievement․ This framework provides practical techniques for teachers, focusing on proven instructional practices․
Marzano’s research-based strategies, outlined in Classroom Instruction That Works, provide educators with evidence-based techniques to enhance student learning․ Developed through analysis of over 100 studies, these strategies focus on specific instructional methods proven to increase student achievement․ Marzano, Pickering, and Pollock collaboratively identified key practices, such as generating hypotheses, using nonlinguistic representations, and summarization, which are foundational to effective teaching; The strategies emphasize active student engagement, critical thinking, and structured lesson planning․ By translating research into actionable techniques, Marzano’s work has significantly influenced educational practices, offering teachers practical tools to create impactful learning experiences․
1․2 Key Concepts and Principles
Central to Marzano’s approach are key concepts that guide effective instruction․ These include the importance of clear learning goals, structured lessons, and formative assessments․ The research highlights the value of student engagement, critical thinking, and differentiated instruction․ Techniques such as generating hypotheses, using nonlinguistic representations, and summarization are emphasized to deepen understanding․ Marzano’s framework also stresses the role of classroom management and the need for a supportive learning environment․ By focusing on these principles, educators can create a structured yet flexible classroom that fosters academic success and personal growth for all students, ensuring that research-based strategies are effectively implemented to enhance achievement․

Research-Based Strategies for Increasing Student Achievement
This chapter discusses research-based strategies, such as generating hypotheses, nonlinguistic representations, summarization, and self-questioning, proven to enhance student learning and achievement in Marzano’s framework․
2․1 Generating and Testing Hypotheses
Generating and testing hypotheses is a powerful strategy that engages students in critical thinking․ By encouraging students to form and test hypotheses, teachers foster deeper understanding and analytical skills․ This approach aligns with Marzano’s research, which highlights its effectiveness in increasing student achievement․ Hypotheses generation allows students to explore concepts actively, making learning more interactive and meaningful․ Teachers can guide this process through structured activities, ensuring students learn to articulate their thoughts and evaluate evidence․ This method not only enhances comprehension but also prepares students for real-world problem-solving, making it a valuable instructional tool in the classroom․
2․2 Using Nonlinguistic Representations
Nonlinguistic representations are visual or physical tools that help students grasp complex concepts․ Marzano’s research highlights their effectiveness in enhancing understanding and retention․ Techniques include images, graphs, and physical models, which make abstract ideas tangible․ These representations allow students to visualize relationships and processes, aiding in deeper comprehension․ For example, using diagrams to illustrate scientific processes or creating concept maps to organize information․ This approach caters to visual learners and reinforces learning across subjects․ By incorporating nonlinguistic representations, teachers can make instruction more engaging and accessible, leading to improved student achievement and a richer learning experience․
2․3 Summarization and Self-Questioning
Summarization and self-questioning are powerful strategies that encourage students to engage deeply with content․ Summarization involves condensing information into concise, meaningful statements, helping students identify key ideas and retain knowledge․ Self-questioning promotes active thinking, as students generate and answer questions about the material․ These techniques enhance comprehension, critical thinking, and metacognition․ Teachers can model summarization by highlighting main ideas and asking guiding questions․ Encouraging students to pose questions fosters curiosity and clarifies understanding․ Regular practice of these strategies strengthens learning outcomes and prepares students for independent thinking and problem-solving․
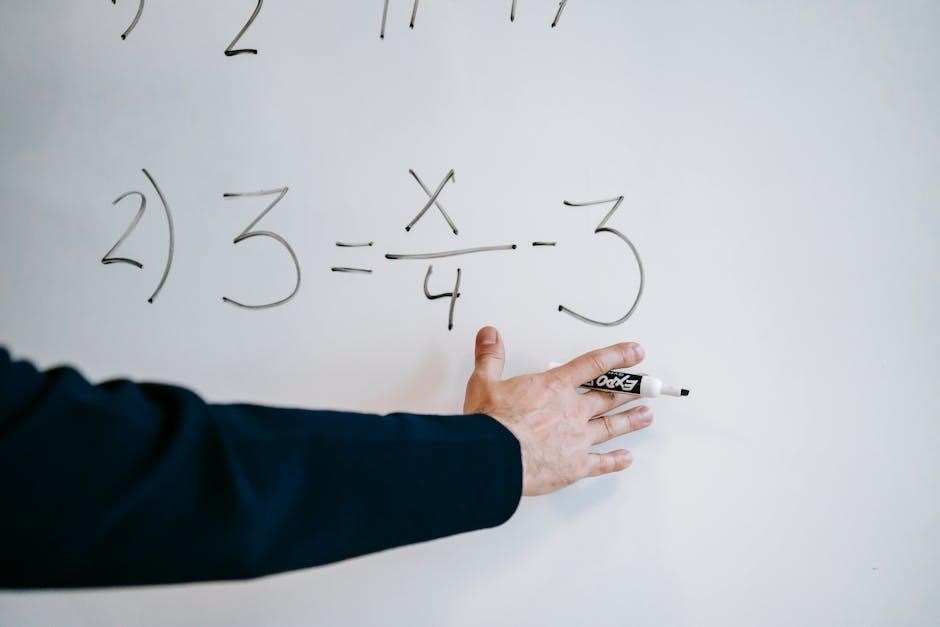
Effective Lesson Planning and Delivery
Effective lesson planning involves clear objectives, engaging activities, and structured delivery, ensuring alignment with learning goals and fostering student understanding and participation․
3․1 The Four-Phase Questioning Sequence
The Four-Phase Questioning Sequence is a structured approach to engage students in critical thinking․ It begins with focus questions to introduce concepts, followed by rehearse questions to model understanding․ The sequence then progresses to guided practice questions, allowing students to apply knowledge with support, and concludes with independent practice questions for self-directed application․ This method ensures a gradual release of responsibility, fostering deeper comprehension and problem-solving skills․ By aligning questions with learning objectives, teachers can enhance rigor and student engagement, making this sequence a cornerstone of effective lesson delivery․
3․2 Graphic Organizers and Guiding Questions
Graphic organizers are visual tools designed to help students structure and organize information effectively․ They enhance comprehension by making abstract concepts concrete․ Common examples include Venn diagrams, concept maps, and flowcharts․ When paired with guiding questions, these tools promote critical thinking and active learning․ Guiding questions are open-ended and strategically posed to encourage students to explore relationships between ideas․ Teachers use them before and during lessons to activate prior knowledge and guide discovery․ Together, graphic organizers and guiding questions create a scaffolded learning environment, enabling students to construct meaning and retain information more effectively․ This dual approach is a cornerstone of Marzano’s strategies for enhancing engagement and understanding․

Classroom Management and Instructional Strategies
Classroom management involves creating a structured, respectful environment to minimize disruptions and maximize learning․ Effective instructional strategies engage students and promote active participation in lessons․
4․1 components of Effective Classroom Management
4․1 Components of Effective Classroom Management
Effective classroom management involves creating a structured, supportive environment that minimizes disruptions and maximizes learning․ Key components include establishing clear expectations, fostering positive relationships, and using proactive strategies to manage behavior․ Teachers should create a respectful atmosphere where students feel safe and engaged․ Active supervision, clear communication, and consistent consequences are essential for maintaining order․ Additionally, incorporating student-centered practices, such as choice and autonomy, can enhance motivation and responsibility․ By combining these elements, educators can build a well-managed classroom that promotes academic success and social growth for all students․
4․2 Enhancing Student Engagement and Participation

Enhancing student engagement and participation is crucial for fostering an active learning environment․ Marzano’s strategies suggest using techniques like generating hypotheses, nonlinguistic representations, and summarization to encourage critical thinking․ Teachers can incorporate graphic organizers to visually structure content, making it more accessible․ Guiding questions can also stimulate curiosity and direct focus․ Encouraging self-questioning and think-alouds helps students articulate their thoughts, increasing involvement․ Additionally, providing opportunities for rehearsal and practice under supervision reinforces understanding․ By integrating these methods, educators can create engaging lessons that cater to diverse learners, ensuring all students are motivated and actively participate in their educational journey․
Differentiation and Support for Diverse Learners
Marzano’s strategies emphasize tailoring instruction to meet diverse learning needs, including English language learners, through differentiated practices, think-alouds, and inferencing to enhance comprehension and engagement․
5․1 Strategies for English Language Learners
Marzano’s strategies for English Language Learners (ELLs) focus on scaffolding language acquisition․ Techniques include using visual aids, graphic organizers, and think-alouds to build vocabulary and comprehension․ Providing clear explanations and modeling tasks helps ELLs grasp complex concepts․ Incorporating students’ native languages and cultural backgrounds enhances engagement and understanding․ Marzano also emphasizes the importance of gradual release of responsibility, allowing ELLs to practice language skills in structured and supportive environments․ These approaches ensure that ELLs receive targeted support to succeed academically while developing their English proficiency․
5․2 Using Think-Alouds and Inferencing
Think-alouds and inferencing are powerful strategies to engage students in critical thinking․ Teachers model their thought processes aloud, demonstrating problem-solving and decision-making․ This makes abstract thinking visible and accessible․ Inferencing encourages students to draw conclusions from evidence, enhancing comprehension and reasoning․ Both techniques foster active participation and deeper understanding of content․ By scaffolding these skills, teachers help students develop the ability to think critically and express their thoughts clearly․ These strategies are particularly effective for diverse learners, as they provide explicit modeling and support for complex cognitive tasks․
Implementation and Professional Development
This section explores strategies for translating research into practice, fostering professional learning communities, and promoting continuous improvement to enhance instructional effectiveness and teacher development․
6․1 Translating Research into Practice
Translating research into practice involves applying evidence-based strategies to classroom teaching․ Marzano’s work emphasizes research-backed methods such as generating hypotheses and using nonlinguistic representations․ Teachers benefit from professional development that helps them understand and implement these strategies effectively․ Continuous improvement and collaboration are key to ensuring that research is not just theoretical but actively enhances student learning․ By bridging the gap between research and practice, educators can create engaging and effective learning environments that lead to improved student outcomes․
6․2 Mastery Teaching and Continuous Improvement
Mastery teaching focuses on helping students achieve deep understanding through structured lessons and active engagement․ Marzano emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement, where teachers reflect on their practices and refine them for better results․ This approach encourages teachers to use data and feedback to identify areas for growth․ By fostering a culture of improvement, educators can ensure that their strategies remain effective and aligned with student needs․ This process not only enhances teaching skills but also leads to higher levels of student achievement and engagement․





